Skin cancer is one of the most common types of cancer, but it is also one of the most preventable. Understanding the different types of skin cancer, knowing the risk factors, and learning how to protect yourself can make a big difference. This article will guide you through the essentials of skin cancer, from prevention and early detection to treatment options and living with the disease.
Key Takeaways
- Skin cancer is highly preventable with proper sun protection and lifestyle choices.
- Early detection through regular skin checks can significantly increase the chances of successful treatment.
- There are various types of skin cancer, each with unique characteristics and treatment options.
- Risk factors for skin cancer include UV exposure, genetic predisposition, and certain lifestyle choices.
- Advancements in treatment and research are continually improving outcomes for skin cancer patients.
Types of Skin Cancer
Skin cancer is a common and potentially serious condition. Understanding the different types can help in early detection and treatment. Here are the main types of skin cancer:
Basal Cell Carcinoma
Basal cell carcinoma (BCC) is the most common type of skin cancer. It often appears as a slightly transparent bump on the skin, though it can take other forms. BCC usually occurs in areas exposed to the sun, such as the head and neck. While it grows slowly and rarely spreads to other parts of the body, early treatment is essential to prevent extensive damage.
Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) is the second most common type of skin cancer. It typically appears as a red, scaly patch, an open sore, or a wart-like growth. SCC can develop on any part of the body but is most common in sun-exposed areas. Unlike BCC, SCC can spread to other parts of the body if not treated promptly.
Melanoma
Melanoma is the most dangerous form of skin cancer. It can develop in an existing mole or appear as a new dark spot on the skin. Melanomas often have irregular shapes and multiple colors. Early detection is crucial, as melanoma can spread rapidly to other organs. The ABCDE rule (Asymmetry, Border, Color, Diameter, Evolving) can help identify suspicious moles.
Rare Skin Cancers
There are several less common types of skin cancer, including:
- Merkel cell carcinoma: A fast-growing cancer that usually appears as a firm, red or purple nodule.
- Kaposi’s sarcoma: Often associated with immune deficiencies, it appears as red or purple patches on the skin or mucous membranes.
- Sebaceous gland carcinoma: An aggressive cancer originating in the oil glands, often appearing as a hard, painless nodule.
Early detection and treatment of skin cancer can significantly improve outcomes. Regular skin checks and awareness of changes in your skin are vital.
For more information, visit the American Academy of Dermatology or the Skin Cancer Foundation.
Risk Factors for Skin Cancer

Ultraviolet Radiation Exposure
Ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun is the leading cause of skin cancer. UV rays can damage the DNA in skin cells, leading to mutations that may result in cancer. It’s important to note that UV radiation can penetrate clouds and glass, and it can reflect off surfaces like water, sand, and snow. This means you can still get sunburned on cloudy days or while in the shade if you’re near reflective surfaces.
Genetic Predisposition
Your genes play a significant role in your risk for skin cancer. If you have a family history of skin cancer, especially melanoma, your risk is higher. Certain genetic conditions, such as dysplastic nevus syndrome, can also increase your risk. People with fair skin, light hair, and light eyes are more prone to skin cancer due to their lower levels of melanin, which provides some protection against UV radiation.
Environmental Factors
Exposure to certain chemicals and pollutants can increase your risk of developing skin cancer. For example, arsenic exposure, often through contaminated water or occupational hazards, is a known risk factor. Additionally, living in areas with high levels of air pollution can contribute to skin damage and increase cancer risk.
Lifestyle Choices
Certain lifestyle choices can significantly impact your risk of skin cancer. Frequent use of tanning beds exposes your skin to harmful UV radiation, increasing your risk. Smoking has also been linked to a higher risk of squamous cell carcinoma. Moreover, a diet low in antioxidants and high in processed foods can weaken your skin’s ability to repair itself, making it more susceptible to cancer.
Regular skin checks are crucial for early detection of skin issues, especially skin cancer. If you notice any changes in your skin, such as new moles or changes in existing ones, it’s important to consult a dermatologist.
Preventive Measures Against Skin Cancer
Sun Protection Strategies
Protecting your skin from the sun is the most effective way to prevent skin cancer. Ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun can cause significant damage to your skin. Here are some strategies to protect yourself:
- Seek shade, especially between 10 AM and 4 PM when the sun’s rays are strongest.
- Wear sun-protective clothing, such as long-sleeved shirts, pants, a wide-brimmed hat, and sunglasses with UV protection.
- Apply a broad-spectrum sunscreen with an SPF of 30 or higher. Reapply every two hours, or more often if swimming or sweating.
- Avoid tanning beds, as they also emit harmful UV radiation.
Diet and Lifestyle Modifications
A healthy diet and lifestyle can also play a role in preventing skin cancer. Consider the following tips:
- Eat a diet rich in fruits and vegetables, which contain antioxidants that can help protect your skin.
- Maintain a healthy weight and stay physically active.
- Avoid smoking and limit alcohol consumption.
Regular Skin Examinations
Regular skin checks can help detect skin cancer early when it is most treatable. Here’s what you can do:
- Perform a self-examination of your skin once a month. Look for new or changing moles, spots, or lesions.
- Schedule annual skin exams with a dermatologist, especially if you have a history of skin cancer or other risk factors.
Vaccinations and Medications
Certain vaccinations and medications can reduce the risk of skin cancer:
- The HPV vaccine can help prevent cancers caused by the human papillomavirus, including some skin cancers.
- Some medications, like retinoids, may reduce the risk of certain skin cancers in high-risk individuals. Consult your doctor for advice.
Taking proactive steps to protect your skin and maintain a healthy lifestyle can significantly reduce your risk of developing skin cancer. Regular check-ups and staying informed about the latest prevention strategies are key to staying safe.
Early Detection of Skin Cancer
Recognizing Symptoms
Recognizing the early signs of skin cancer is crucial for effective treatment. Most skin cancers can be found early by examining your skin regularly. Look for new or changing moles, sores that don’t heal, or any unusual skin changes. If you notice anything suspicious, see a doctor right away.
Self-Examination Techniques
Performing regular self-exams can help you catch skin cancer early. Here’s how to do a thorough skin check:
- Examine your skin in a well-lit room using a full-length mirror.
- Check all areas of your body, including hard-to-see spots like your back and scalp. Use a hand mirror if needed.
- Note any new or changing moles or spots.
- Consider creating a "body map" to track changes over time.
- Ask a family member or friend to help check areas you can’t see.
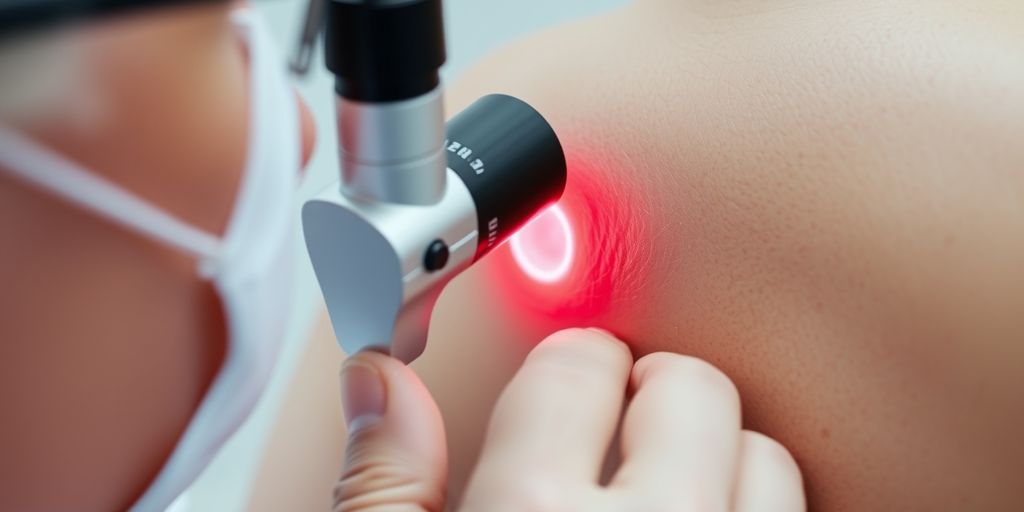
Professional Screenings
Annual skin exams by a dermatologist are recommended, especially if you have risk factors for skin cancer. A dermatologist can identify suspicious areas that you might miss. Early diagnosis through professional screenings can significantly improve treatment outcomes.
Diagnostic Tools
If a suspicious area is found, your doctor may use several diagnostic tools to determine if it’s cancerous:
- Skin biopsy: Removing a small sample of skin for lab testing.
- Dermatoscopy: Using a special magnifying device to examine the skin in detail.
- Imaging tests: Such as ultrasound or MRI, to check if cancer has spread.
Regular self-exams and professional screenings are key to catching skin cancer early. Don’t wait—examine your skin frequently and consult a doctor if you notice any changes.
Treatment Options for Skin Cancer
Surgical Procedures
Surgery is often the first line of treatment for many types of skin cancer. Excisional surgery involves cutting out the cancerous tissue along with a margin of healthy skin. For more complex cases, Mohs surgery is used. This technique removes the cancer layer by layer, examining each under a microscope until no abnormal cells remain. This method is particularly useful for cancers in sensitive areas like the face.
Radiation Therapy
Radiation therapy uses high-energy beams, such as X-rays, to kill cancer cells. It is often used when surgery isn’t an option or to target cancer cells left behind after surgery. This treatment is usually spread out over several sessions to minimize damage to healthy tissue.
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy involves using drugs to kill cancer cells. For skin cancers limited to the top layer of skin, topical treatments like creams or lotions may be effective. Systemic chemotherapy, which affects the whole body, is used for more advanced cases where cancer has spread to other parts of the body.
Targeted and Immunotherapy
Targeted therapy focuses on specific molecules involved in cancer growth. These treatments can block the growth and spread of cancer cells while minimizing damage to normal cells. Immunotherapy, on the other hand, boosts the body’s immune system to fight cancer. Drugs like checkpoint inhibitors help the immune system recognize and attack cancer cells more effectively.
Early detection and treatment are crucial for the best outcomes in skin cancer care. Always consult with a healthcare provider to determine the most appropriate treatment plan for your specific condition.
Managing Advanced Skin Cancer
Palliative Care
Palliative care focuses on improving the quality of life for patients with advanced skin cancer. This type of care aims to relieve symptoms and reduce suffering. It is essential for patients who may not be able to achieve a cure. Palliative care can include pain management, emotional support, and assistance with daily activities.
Clinical Trials
Clinical trials offer patients access to new and experimental treatments that are not yet widely available. Participating in a clinical trial can provide hope and potential benefits for those with advanced skin cancer. Patients should discuss with their healthcare providers to determine if a clinical trial is a suitable option.
Supportive Therapies
Supportive therapies are designed to help manage the side effects of cancer treatment and improve overall well-being. These therapies can include physical therapy, nutritional support, and counseling services. They play a crucial role in helping patients maintain their strength and quality of life during treatment.
Patient Resources
Numerous resources are available to support patients with advanced skin cancer. These can include support groups, online communities, and educational materials. Accessing these resources can provide valuable information and emotional support for both patients and their families.
Managing advanced skin cancer requires a comprehensive approach that includes medical treatment, palliative care, and supportive therapies. By utilizing available resources and exploring clinical trials, patients can find hope and improve their quality of life.
Skin Cancer in Different Populations
Skin Cancer in Children
Skin cancer is rare in children, but it can still occur. Early detection is crucial for effective treatment. Parents should regularly check their children’s skin for any unusual moles or spots and consult a doctor if they notice anything suspicious. Pediatricians can also provide guidance on sun protection for kids, such as using sunscreen and wearing protective clothing.
Skin Cancer in Elderly
The risk of skin cancer increases with age. Older adults are more likely to develop skin cancer due to cumulative sun exposure over their lifetime. Regular skin checks by a healthcare professional are essential for early detection. Elderly individuals should also be vigilant about protecting their skin from the sun, even if they have not had issues in the past.
Skin Cancer in People of Color
People of color are less likely to get skin cancer than those with lighter skin, but when they do, it is often diagnosed at a later stage. This can lead to worse outcomes. It’s important for people of all skin tones to perform regular self-examinations and seek medical advice if they notice any changes in their skin. Education on the signs of skin cancer and the importance of sun protection is vital for this group.
Gender Differences in Skin Cancer
Men are more likely to develop skin cancer than women, possibly due to more frequent sun exposure and less use of sun protection. Women, however, are more likely to check their skin regularly and seek medical advice sooner. Both men and women should be aware of the risks and take preventive measures, such as using sunscreen and wearing protective clothing.
Impact of Skin Cancer Globally
Incidence and Mortality Rates
Skin cancer is one of the most common cancers worldwide. The incidence of skin cancer has been rising steadily over the past few decades. This increase is largely attributed to higher exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun and tanning beds. Mortality rates vary by type of skin cancer, with melanoma being the most deadly. Early detection and treatment are crucial for improving survival rates.
Economic Burden
The economic impact of skin cancer is significant. Costs include medical treatments, hospital stays, and lost productivity. In countries with high healthcare costs, the financial burden on patients and healthcare systems can be substantial. Preventive measures, such as public education on sun safety, can help reduce these costs.
Healthcare Disparities
There are notable disparities in skin cancer outcomes based on geographic location, socioeconomic status, and access to healthcare. People in low-income regions often have limited access to dermatological care and early detection services, leading to worse outcomes. Efforts to improve healthcare access and education in these areas are essential.
Global Prevention Initiatives
Several global initiatives aim to reduce the incidence of skin cancer. These include public awareness campaigns about the dangers of UV exposure, promoting the use of sunscreen, and encouraging regular skin checks. International collaborations, such as the World Health Organization’s efforts, are crucial in spreading effective prevention strategies worldwide.
Skin cancer is a growing global health issue that requires coordinated efforts for prevention, early detection, and treatment. By addressing healthcare disparities and promoting awareness, we can work towards reducing the impact of this disease on a global scale.
Innovations in Skin Cancer Research

Genetic Research
Genetic research is making strides in understanding skin cancer. Scientists are identifying specific genes that increase the risk of developing skin cancer. This knowledge helps in creating targeted therapies and personalized treatment plans. Genetic testing can now identify individuals at higher risk, allowing for early intervention and monitoring.
New Treatment Modalities
New treatment methods are continually being developed. These include advanced surgical techniques, improved radiation therapy, and innovative drug therapies. One promising area is the use of biological therapies that harness the body’s immune system to fight cancer cells more effectively.
Technological Advances
Technology is playing a crucial role in skin cancer research. High-resolution imaging and AI-driven diagnostic tools are improving the accuracy of skin cancer detection. These technologies enable doctors to identify and treat skin cancer at earlier stages, significantly improving patient outcomes.
Future Directions
The future of skin cancer research looks promising. Researchers are exploring the potential of nanotechnology in delivering targeted treatments directly to cancer cells. Additionally, ongoing clinical trials are testing new drugs and treatment combinations, aiming to find more effective and less invasive options for patients.
The continuous advancements in skin cancer research bring hope for better prevention, early detection, and treatment options, ultimately aiming to reduce the global burden of this disease.
Living with Skin Cancer

Emotional and Psychological Support
Living with skin cancer can be emotionally challenging. It’s important to seek support from friends, family, or professional counselors. Support groups, both in-person and online, can provide a sense of community and understanding. Don’t hesitate to talk about your feelings and fears; sharing can be a powerful tool for coping.
Lifestyle Adjustments
Adapting your lifestyle is crucial when living with skin cancer. Here are some tips:
- Sun Protection: Always use sunscreen with a high SPF, wear protective clothing, and avoid peak sun hours.
- Healthy Diet: Eating a balanced diet rich in fruits and vegetables can boost your immune system.
- Regular Exercise: Staying active helps improve overall health and well-being.
Survivorship Care Plans
After treatment, a survivorship care plan is essential. This plan includes:
- Follow-up Appointments: Regular check-ups with your healthcare provider to monitor for any signs of recurrence.
- Health Maintenance: Guidelines for maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including diet and exercise recommendations.
- Symptom Management: Strategies to manage any ongoing symptoms or side effects from treatment.
Community and Online Resources
Numerous resources are available to help you navigate life with skin cancer. Some useful options include:
- Support Groups: Join local or online support groups to connect with others who understand your journey.
- Educational Websites: Websites like the American Cancer Society offer valuable information and resources.
- Hotlines: Many organizations provide hotlines for immediate support and information.
Living with skin cancer requires a comprehensive approach that includes emotional support, lifestyle adjustments, and access to resources. Remember, you are not alone in this journey.
Conclusion
Understanding skin cancer is crucial for everyone. By knowing the risks, taking preventive steps, and seeking early treatment, we can significantly reduce the impact of this disease. Remember to protect your skin from the sun, avoid tanning beds, and regularly check your skin for any changes. Early detection and proper treatment can save lives. Stay informed and proactive about your skin health to ensure a brighter, healthier future.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the main types of skin cancer?
The main types of skin cancer are Basal Cell Carcinoma, Squamous Cell Carcinoma, and Melanoma. There are also some rare types like Merkel Cell Carcinoma and Dermatofibrosarcoma Protuberans.
How can I reduce my risk of getting skin cancer?
You can lower your risk by avoiding tobacco, maintaining a healthy weight, eating fruits and vegetables, exercising regularly, limiting alcohol, getting vaccinated against HPV and hepatitis B, and protecting yourself from UV radiation.
What are the risk factors for skin cancer?
Risk factors include exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation, genetic predisposition, environmental factors, and lifestyle choices like tanning and smoking.
How can I protect myself from the sun?
To protect yourself, seek shade, wear protective clothing, use sunscreen with SPF 30 or higher, and avoid tanning beds. Also, wear sunglasses and a wide-brimmed hat.
What are the symptoms of skin cancer?
Symptoms can include new growths, sores that don’t heal, changes in existing moles, and unusual skin changes. It’s important to see a doctor if you notice any of these signs.
How is skin cancer diagnosed?
Skin cancer is usually diagnosed through a skin examination and a biopsy, where a small sample of skin is taken and tested in a lab.
What treatments are available for skin cancer?
Treatment options include surgical procedures, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, and newer treatments like targeted therapy and immunotherapy.
Can skin cancer be cured if detected early?
Yes, if skin cancer is detected early, it is often highly treatable and can be cured. Early detection and treatment are crucial.