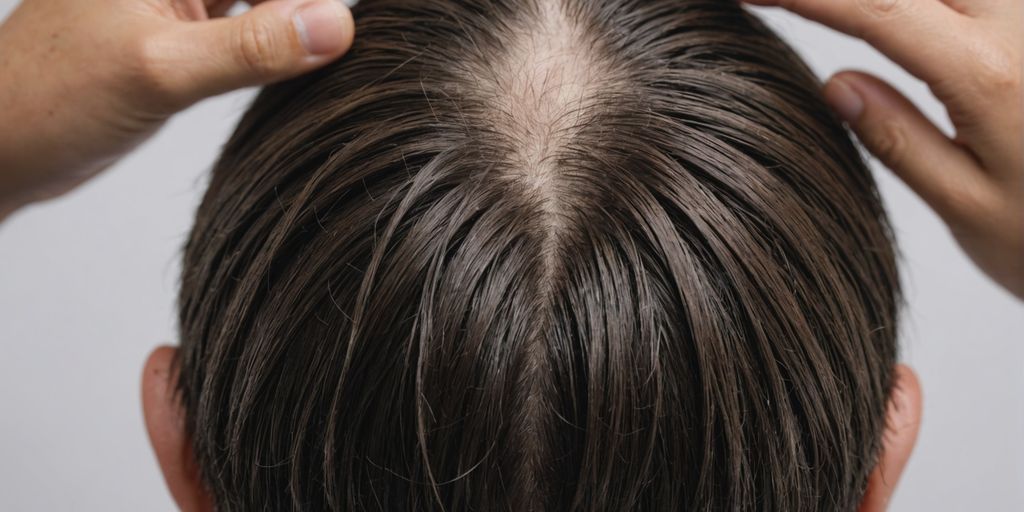
Hair loss is a common issue that can affect anyone, regardless of age or gender. While it’s normal to lose a few strands of hair daily, excessive hair loss can be concerning. Understanding the causes can help in finding the right treatment. Here are the ten most common reasons why people experience hair loss.
Key Takeaways
- Hair loss can result from genetic factors, hormonal changes, stress, and nutritional deficiencies.
- Certain medications and tight hairstyles can lead to hair thinning or baldness.
- Conditions like alopecia areata, tinea capitis, and lupus erythematosus can cause significant hair loss.
Androgenetic Alopecia
Androgenetic alopecia (AGA) is the most common form of hair loss worldwide. It is a chronic condition influenced by both genetics and environmental factors. In men, AGA typically starts with a receding hairline and thinning at the crown. Women, on the other hand, usually experience diffuse thinning across the scalp while maintaining their frontal hairline.
Treatment Options
Several treatments are available for managing AGA:
- Topical Minoxidil: This FDA-approved treatment helps stimulate hair growth and slow down hair loss.
- Oral Finasteride: Another FDA-approved option, primarily for men, that reduces hair loss by blocking the hormone responsible for follicle shrinkage.
- Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP): This involves injecting plasma from the patient’s blood into the scalp to promote hair growth.
- Low-Level Light Therapy: A non-invasive treatment that uses light to stimulate hair follicles.
- Nutritional Supplements: Certain vitamins and minerals can support hair health.
Expert Recommendations
An expert consensus by Spanish dermatologists offers treatment recommendations for androgenetic alopecia, emphasizing the importance of early intervention and a combination of therapies for optimal results.
Androgenetic alopecia can start at any age after puberty, but it is more common as people get older. Hormones, especially after menopause in women, can play a significant role in its development.
Additional Therapies
- Hair Transplant: A surgical option where healthy hair follicles are moved from one part of the scalp to another.
- Spironolactone: This medication may help reduce hair loss in women by addressing hormonal imbalances.
- Laser Therapy: Low-level lasers are used to stimulate hair growth.
Early diagnosis and a tailored treatment plan are crucial for managing androgenetic alopecia effectively.
Hormonal Fluctuations
Hormonal changes can have a profound influence on hair health. These fluctuations can be due to various life stages and conditions.
- Pregnancy and Childbirth: Many women experience hair loss after giving birth due to a drop in estrogen levels.
- Menopause: Hormonal shifts during menopause can lead to thinning hair.
- Thyroid Disorders: Both hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism can disrupt hair growth cycles.
- Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS): Higher androgen levels in PCOS can cause female-pattern hair loss.
- Medication Changes: Stopping or starting medications, like birth control pills, can affect hormone levels and lead to hair loss.
Hormonal imbalances occur when there is too much or too little of a hormone in the blood. Common symptoms include weight changes, lower sex drive, and acne, but they can also lead to hair loss.
Stressful events or periods of intense stress can trigger hair shedding, while an imbalanced diet lacking in essential nutrients like iron and protein may also contribute to hair loss. Fortunately, in most cases, proper treatment can slow down or reverse the hair loss.
Stress

Stress can be a significant factor in hair loss. One of the most common stress-related hair loss conditions is telogen effluvium. This condition usually occurs a few months after a person experiences a traumatic event or high levels of stress. During telogen effluvium, hair shedding becomes noticeable, but it is typically temporary.
Symptoms
- Sudden hair shedding
- Hair falling out in clumps
- Noticeable thinning of hair
Causes
Stressful life events such as:
- Losing a loved one
- Undergoing surgery
- Being diagnosed with a serious illness
Recovery
Most cases of telogen effluvium resolve on their own within 6 to 9 months as the body readjusts. Hair gradually stops falling out and begins to regrow.
It’s important to remember that telogen effluvium is temporary and you will not go bald from it. Your hair will come back.
Managing Stress-Related Hair Loss
- Identify and reduce stressors where possible
- Consider Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT)
- Engage in regular physical activity
In some cases, temporary hair shedding can occur after a fever, illness, or stress. For example, studies have shown that about 20% of people who had COVID-19 later developed temporary hair shedding. Removing the cause of stress is the best approach, but when this isn’t possible, managing stress through therapy and exercise can help.
When to See a Doctor
If hair loss persists beyond a few months or is accompanied by other symptoms, it is advisable to consult a healthcare provider to rule out other underlying conditions.
Nutritional Deficiencies

Nutritional deficiencies can play a significant role in hair loss. Low levels of essential vitamins and minerals can weaken hair, making it more prone to shedding. Key nutrients like vitamin D, iron, vitamin C, and B vitamins are crucial for maintaining healthy hair.
- Vitamin D: Important for creating new hair follicles. A deficiency can lead to hair thinning.
- Iron: Helps carry oxygen to hair follicles, promoting growth. Low iron levels are a common cause of hair loss.
- Vitamin C: Aids in the absorption of iron and helps in collagen production, which strengthens hair.
- B Vitamins: Essential for overall hair health. Deficiencies in B vitamins can lead to hair loss.
Eating a well-balanced diet rich in these nutrients is the best way to ensure your hair gets what it needs. Foods like legumes, leafy greens, and lean proteins are excellent choices.
If you suspect a nutritional deficiency, it’s important to consult with a healthcare provider. They can perform blood tests to identify any deficiencies and recommend appropriate supplements or dietary changes.
Medications
Certain medications can lead to hair loss as a side effect. This can be distressing, but understanding which drugs might cause this can help you manage the issue better.
Some drugs that may cause hair loss include:
- Antidepressants
- Monoclonal antibodies
- Antihypertensives
- Anticonvulsants
- Arthritis medications
If you suspect your medication is causing hair loss, consult your doctor. They might adjust your dosage or switch you to a different drug. Always seek medical advice before making any changes to your medication regimen.
Hair loss from medications is usually temporary. Once you stop taking the drug, your hair often grows back.
Traction Alopecia
Traction alopecia is a type of hair loss caused by hairstyles or other things that pull on your hair. This is most often due to wearing tight hairstyles, such as braids, ponytails, and cornrows. Early signs include thinning at the frontal hairline, which can progress to more severe hair loss if not addressed.
Causes
- Tight hairstyles (braids, ponytails, cornrows)
- Hair extensions or weaves
- Frequent use of hair rollers
- Wearing helmets or headgear that pulls on the hair
Symptoms
- Thinning hair, especially around the hairline
- Small bumps on the scalp
- Redness or soreness on the scalp
- Broken hairs
Treatment
- Stop wearing tight hairstyles: The first step is to stop any hairstyle that pulls on the hair.
- Use gentle hair care products: Switch to mild shampoos and conditioners.
- Topical treatments: Corticosteroids or minoxidil may be recommended by a doctor.
- Supplements: Biotin supplements can help strengthen hair.
Traction alopecia is preventable and treatable if caught early. Avoiding tight hairstyles and taking good care of your hair can make a big difference.
Prevention
- Avoid tight hairstyles
- Give your hair breaks between styles
- Use soft hair ties instead of rubber bands
- Be gentle when brushing and styling your hair
Alopecia Areata
Alopecia Areata is a chronic autoimmune disorder that causes hair loss. It affects about 2% of the population. The condition can lead to different types of hair loss, from small, round patches on the scalp to complete loss of hair on the scalp (alopecia totalis) or even the entire body (alopecia universalis).
The exact cause of Alopecia Areata is not fully understood, but it is believed to occur when the immune system mistakenly attacks hair follicles. This disrupts hair growth and leads to hair loss.
Symptoms
- Sudden hair loss in small, round patches on the scalp
- Patches may overlap and become more noticeable
- In severe cases, complete loss of hair on the scalp or body
Treatment Options
- Topical and intralesional steroid injections: These can help reduce inflammation and promote hair growth.
- Immunosuppressants: Medications that suppress the immune system can be effective.
- Emerging treatments: New drugs like Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitors show promise and have received FDA approval.
Living with Alopecia Areata can be challenging, but treatments are available that can help manage the condition and promote hair regrowth.
Tinea Capitis
Tinea capitis, also known as scalp ringworm, is a highly contagious fungal infection. It often leads to round patches of hair loss, accompanied by scaling and redness on the scalp.
Symptoms
- Scaly, discolored ring-like patches on the scalp
- Patches of hair loss that grow over time
- Oozing blisters
- Itchiness
- Brittle hair that breaks easily
Diagnosis
Doctors typically diagnose tinea capitis through:
- Clinical examination
- KOH analysis
- Fungal culture
Treatment
Prompt treatment is crucial to prevent scarring and further hair loss. The treatment usually involves:
- Oral antifungal medications
- Topical antifungal agents
- Selenium sulfide shampoo
In severe cases, oral corticosteroids may be added to reduce inflammation.
Early diagnosis and treatment are essential to manage tinea capitis effectively and prevent long-term damage.
Trichotillomania
Trichotillomania, also known as hair-pulling disorder, is a condition where individuals feel a strong urge to pull out their own hair. This can lead to noticeable hair loss and can cause significant distress in daily life.
Symptoms
- Repeatedly pulling out hair from the scalp, eyebrows, or other areas of the body.
- Feeling a sense of relief or pleasure after pulling out hair.
- Noticeable hair loss or thinning in the affected areas.
Causes
The exact cause of trichotillomania is not known, but it is often linked to obsessive-compulsive and anxiety disorders. It is more common in women than men.
Treatment
Effective treatment usually involves a combination of cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) and sometimes medications like selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) or antipsychotics. Early recognition and intervention are crucial to prevent chronic hair loss and associated psychological distress.
Understanding trichotillomania (TTM) is essential for early intervention and effective treatment.
Lupus Erythematosus
Lupus erythematosus is an autoimmune disease that can cause hair loss. Discoid lupus erythematosus (DLE) is the most common form affecting the scalp, face, and ears. It starts with purplish spots that turn into coin-shaped plaques. These plaques can lead to scarring alopecia, where hair follicles get clogged and damaged.
Symptoms
- Purplish spots or bumps
- Coin-shaped plaques
- Scarring and hair loss
Treatment
- Photoprotection
- Topical or injected corticosteroids
- Topical calcineurin inhibitors
Early treatment is crucial to prevent permanent hair loss and damage. If you notice any symptoms, consult a doctor immediately.
Lupus is one of the multiple autoimmune diseases that can cause hair loss. Proper diagnosis and treatment can help manage the condition effectively.
Conclusion
Hair loss can be a distressing experience, but understanding its common causes can help in managing and potentially preventing it. From genetic factors to lifestyle choices, many elements play a role in hair health. While some causes, like genetics, are beyond our control, others, such as diet and stress management, can be addressed with lifestyle changes. It’s important to consult with a healthcare provider to determine the specific cause of hair loss and to discuss appropriate treatment options. Remember, early intervention can make a significant difference in maintaining healthy hair.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the most common cause of hair loss?
The most common cause of hair loss is androgenetic alopecia, also known as male or female pattern baldness. It is a genetic condition that usually starts after puberty.
Can stress cause hair loss?
Yes, stress can lead to a type of hair loss called telogen effluvium. This happens when a large number of hair follicles enter the resting phase, causing more hair to fall out.
How can I prevent hair loss?
Preventing hair loss can involve a variety of steps, such as maintaining a healthy diet, avoiding tight hairstyles, and managing stress. If you are experiencing hair loss, it’s best to consult with a healthcare provider for personalized advice.